# 1. 前言
在对组员代码进行审查时,经常碰到看着很不合理的字符串拼接操作,特别是对数组数据操作,也直接一个 for 循环,使用 + 号进行。
甚至有时候还是直接以 Text 作为主体,例如:
for (int i = 0; i < soldierData.Skills.Count; i++) | |
{ | |
m_soldiersDesc.text += soldierData.Skills[i].GetLvDesc(); | |
} |
在这个地方,首先 m_soldiersDesc.text 是一个主体,『+=』操作相当于 取值 + 字符串拼接 + 赋值 + 重构 Text 数据,还是在循环中进行 —— 有多费就不用多说了。
再次对组员进行强调:使用对应指定方式拼接字符串。
项目中其实已有公共的采取 StringBuilder 拼接相关方法,例如:
/// <summary> | |
/// 組合数组 | |
/// </summary> | |
public static string toString<T>(this List<T> list, string split = ",") | |
{ | |
if (!list.valid()) return ""; | |
StringBuilder sbd = new StringBuilder(); | |
for (int i = 0; i < list.Count; i++) sbd.Append(list[i] + (i < list.Count - 1 ? split : "")); | |
return sbd.ToString(); | |
} |
注:虽然该方法是已有的,但是使用的不多 (而且该方法使用 StringBuilder 方式也不大好,例如调用了 StringBuilder Append 还在用 + 号拼接小的),大多都是在搞自我拼接。
所以虽然要求大家使用项目自定义的字符串拼接相关扩展方法,不过这边这块恐怕需要进行优化一下。
# 2. 第一版优化
为此我在这个基础上增加了一份扩展,优化主要有两点:使用 StringBuilder 拼接,且对其进行缓存,每次回收利用。
主要代码如下:
private static StringBuilder _stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(32); | |
private static int _stringCacheLength; | |
private static int _stringCacheTopIndex; | |
/// <summary> | |
/// 将数组组合为字符串 | |
/// </summary> | |
public static string toString<T>(this List<T> list, string split = ",") | |
{ | |
if (!list.valid()) return ""; | |
_stringBuilder.Length = 0; | |
_stringCacheLength = list.Count; | |
_stringCacheTopIndex = _stringCacheLength - 1; | |
for (int i = 0; i < _stringCacheLength; i++) | |
{ | |
_stringBuilder.Append(list[i]); | |
if (i != _stringCacheTopIndex) _stringBuilder.Append(split); | |
} | |
return _stringBuilder.ToString(); | |
} | |
/// <summary> | |
/// 将列表组合为字符串 | |
/// </summary> | |
public static string toString<T>(this List<T> list, RCallback<string, T> getStr, string split = ",") | |
{ | |
if (!list.valid()) return ""; | |
_stringBuilder.Length = 0; | |
_stringCacheLength = list.Count; | |
_stringCacheTopIndex = _stringCacheLength - 1; | |
for (int i = 0; i < _stringCacheLength; i++) | |
{ | |
_stringBuilder.Append(getStr(list[i])); | |
if (i != _stringCacheTopIndex) _stringBuilder.Append(split); | |
} | |
return _stringBuilder.ToString(); | |
} | |
/// <summary> | |
/// 将字典组合为字符串 | |
/// </summary> | |
public static string toString<K, V>(this Dictionary<K, V> dic, string split = ",", Func<K, V, string> getStrCallback = null) | |
{ | |
if (dic.Count < 1) return ""; | |
_stringBuilder.Length = 0; | |
foreach (var item in dic) | |
{ | |
if (getStrCallback == null) | |
_stringBuilder.Append(item.Value); | |
else _stringBuilder.Append(getStrCallback(item.Key, item.Value)); | |
_stringBuilder.Append(split); | |
} | |
_stringBuilder.Remove(_stringBuilder.Length - 1, 1); | |
return _stringBuilder.ToString(); | |
} | |
/// <summary> | |
/// 将数组组合为字符串,换行分割 | |
/// </summary> | |
public static string toStringLine<T>(this T[] arr, RCallback<string, T> getStrCallback = null) | |
{ | |
return arr.toString(Environment.NewLine, getStrCallback); | |
} | |
/// <summary> | |
/// 将列表组合为字符串,换行分割 | |
/// </summary> | |
public static string toStringLine<T>(this List<T> list, RCallback<string, T> getStrCallback = null) | |
{ | |
return list.toString(Environment.NewLine, getStrCallback); | |
} | |
/// <summary> | |
/// 将字典组合为字符串,换行分割 | |
/// </summary> | |
public static string toStringLine<K, V>(this Dictionary<K, V> dic, Func<K, V, string> getStrCallback = null) | |
{ | |
return dic.toString(Environment.NewLine, getStrCallback); | |
} |
主要提供有两种处理方式:一种直接将数组每个数据拼接,另一种会经过回调处理后再拼接。
并支持数组、列表、字典三个常用数据结构内容的拼接。
这里只使用一份 StringBuilder 缓存,是因为考虑到游戏中单线程模式即用就即时返回结果了,没有必要采用对象池模式去缓存多个。
# 3. 性能测试与优化
# 四种拼接方式性能测试
对于性能测试,这里首先以 100000 个放置于一个数组中的随机字符串的拼接为例,分别采用 + 号拼接、string.Join、自定义 StringBuilder、带回调自定义 StringBuilder 四种方式,测试其消耗时长:
private const int TestCount = 100000; | |
// 纯字符串数组 | |
private string[] _strArray; | |
void Start() | |
{ | |
// 初始化测试数据 | |
_strArray = new string[TestCount]; | |
for (int i = 0; i < TestCount; i++) | |
{ | |
_strArray[i] = GetRandomStr(); | |
} | |
// 测试数据填充完毕 | |
//========== | |
Stopwatch stopwatch = Stopwatch.StartNew(); | |
//1. 测试直接拼接数组 | |
stopwatch.Start(); | |
string finalStr = ""; | |
for (int i = 0; i < _strArray.Length; i++) | |
{ | |
finalStr += "," + _strArray[i]; | |
} | |
stopwatch.Stop(); | |
UnityEngine.Debug.Log(finalStr); | |
UnityEngine.Debug.LogWarning(string.Format("直接拼接数组:{0}", stopwatch.Elapsed.ToString())); | |
//2. 测试内部函数 join 拼接数组 | |
stopwatch.Reset(); | |
stopwatch.Start(); | |
finalStr = string.Join(",", _strArray); | |
stopwatch.Stop(); | |
UnityEngine.Debug.Log(finalStr); | |
UnityEngine.Debug.LogWarning(string.Format("string.Join 拼接数组:{0}", stopwatch.Elapsed.ToString())); | |
//3. 测试自定义函数拼接数组 | |
stopwatch.Reset(); | |
stopwatch.Start(); | |
finalStr = _strArray.toString(); | |
stopwatch.Stop(); | |
UnityEngine.Debug.Log(finalStr); | |
UnityEngine.Debug.LogWarning(string.Format("自定义函数拼接数组:{0}", stopwatch.Elapsed.ToString())); | |
//4. 测试带回调自定义函数拼接数组 | |
stopwatch.Reset(); | |
stopwatch.Start(); | |
finalStr = _strArray.toString(",", str => str); | |
stopwatch.Stop(); | |
UnityEngine.Debug.Log(finalStr); | |
UnityEngine.Debug.LogWarning(string.Format("带回调自定义函数拼接数组:{0}", stopwatch.Elapsed.ToString())); | |
} | |
/// <summary> | |
/// 返回一个随机值字符串 | |
/// </summary> | |
private string GetRandomStr() | |
{ | |
return string.Intern(Random.Range(0, 1000000).ToString()); | |
} |
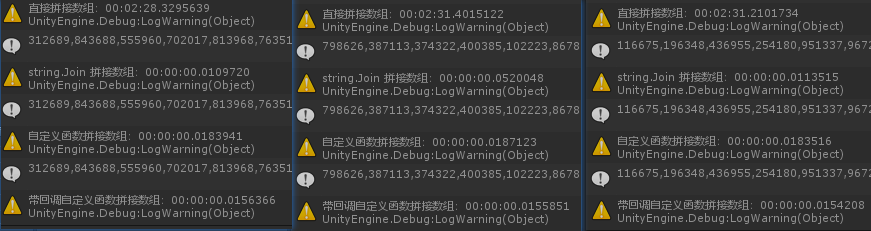
如上图所示,可以看见直接使用 + 号进行拼接的方式,相比另外几种方式其消耗时间可以说是一骑绝尘:可以确定内部基本上没有什么优化的。
严格来说,上述测试方式并不准确,不过这里主要是因为 + 号拼接太过于消耗时间,数据大了电脑跑不动。因此我就仅执行一次大批量测试了 —— 确定这方式真可以丢一边了。
# 平均性能测试
接下来,剔除 + 号拼接方式,对比余下方式去取平均消耗时间。
join、concat、自定义函数、带回调自定义函数分别执行 100 次,取平均时间。
除此之外,增加对 列表、字典、类类型结构测试。
测试代码:
class StrClass | |
{ | |
private string _desStr; | |
public StrClass(string str) | |
{ | |
_desStr = str; | |
} | |
public string GetDes() | |
{ | |
return GetHashCode() + _desStr; | |
} | |
} | |
// 数据长度 | |
private const int TestValueCount = 100000; | |
// 每一轮测试次数,取平均消耗时间 | |
private const int TestNum = 100; | |
// 保存一下结果 | |
private string _logPath; | |
// 纯字符串数组 | |
private string[] _strArray; | |
// 纯字符串列表 | |
private List<string> _strList; | |
// 字典 | |
private Dictionary<int, string> _strDic; | |
// 返回字符串的类结构 | |
private StrClass[] _strClassArray; | |
void Start() | |
{ | |
// 初始化测试数据 | |
_strArray = new string[TestValueCount]; | |
_strList = new List<string>(TestValueCount); | |
_strClassArray = new StrClass[TestValueCount]; | |
_strDic = new Dictionary<int, string>(TestValueCount); | |
for (int i = 0; i < TestValueCount; i++) | |
{ | |
_strArray[i] = GetRandomStr(); | |
_strList.Add(GetRandomStr()); | |
_strClassArray[i] = new StrClass(GetRandomStr()); | |
_strDic[i] = GetRandomStr(); | |
} | |
// 测试数据填充完毕 | |
//========== | |
//Stopwatch stopwatch = Stopwatch.StartNew(); | |
//1. 测试直接拼接数组 | |
//stopwatch.Start(); | |
//string finalStr = ""; | |
//for (int i = 0; i < _strArray.Length; i++) | |
//{ | |
// finalStr += "," + _strArray[i]; | |
//} | |
//stopwatch.Stop(); | |
//UnityEngine.Debug.Log(finalStr); | |
//UnityEngine.Debug.LogWarning (string.Format ("直接拼接数组:{0}", stopwatch.Elapsed.ToString ())); | |
// 清空日志 | |
_logPath = Path.Combine(Application.dataPath, "TestLog.txt"); | |
File.WriteAllText(_logPath, ""); | |
// 测试内部函数 concat 拼接数组 | |
DoTest("string.concat 拼接数组", () => string.Concat(_strArray)); | |
//2. 测试内部函数 join 拼接数组 | |
DoTest("string.Join 拼接数组", () => string.Join(",", _strArray)); | |
//3. 测试自定义函数拼接数组 | |
DoTest("自定义函数拼接数组", () => _strArray.toString()); | |
//4. 测试带回调自定义函数拼接数组 | |
DoTest("带回调自定义函数拼接数组", () => _strArray.toString(",", str => str)); | |
//5. 测试 join 函数拼接列表 | |
DoTest("string.Join 拼接列表", () => _strList.toString()); | |
//6. 测试自定义函数拼接列表 | |
DoTest("自定义函数拼接列表", () => _strList.toString()); | |
//7. 测试带回调自定义函数拼接列表 | |
DoTest("带回调自定义函数拼接列表", () => _strList.toString()); | |
//8. 测试自定义函数拼接类类型 | |
DoTest("自定义函数拼接类类型", () => _strClassArray.toString(",", data => data.GetDes())); | |
//9. 测试自定义函数拼接字典 | |
DoTest("自定义函数拼接字典", () => _strDic.toString()); | |
//10. 测试自定义函数拼接字典 | |
DoTest("自定义函数拼接字典(带回调操作)", () => _strDic.toString(",", (k, v) => k + v)); | |
} | |
/// <summary> | |
/// 执行一轮对 callback 运行测试 | |
/// </summary> | |
private void DoTest(string title, Action callback) | |
{ | |
Stopwatch stopwatch = Stopwatch.StartNew(); | |
long totalTime = 0; | |
for (int i = 0; i < TestNum; i++) | |
{ | |
stopwatch.Reset(); | |
stopwatch.Start(); | |
callback(); | |
stopwatch.Stop(); | |
totalTime += stopwatch.ElapsedTicks; | |
} | |
TimeSpan span = new TimeSpan(totalTime); | |
string log = string.Format("* {0}:{1}秒{2}毫秒\n", title, span.Seconds, span.Milliseconds); | |
File.AppendAllText(_logPath, log); | |
UnityEngine.Debug.LogWarning(log); | |
} | |
/// <summary> | |
/// 返回一个随机值字符串 | |
/// </summary> | |
private string GetRandomStr() | |
{ | |
return string.Intern(UnityEngine.Random.Range(0, 1000000).ToString()); | |
} |
结果如下:
- string.concat 拼接数组:00:00:00.0099083
- string.Join 拼接数组:00:00:00.0132115
- 自定义函数拼接数组:00:00:00.0179701
- 带回调自定义函数拼接数组:00:00:00.0175816
- string.Join 拼接列表:00:00:00.0184016
- 自定义函数拼接列表:00:00:00.0185559
- 带回调自定义函数拼接列表:00:00:00.0180418
- 自定义函数拼接类类型:00:00:00.1013892
- 自定义函数拼接字典:00:00:00.0224806
- 自定义函数拼接字典 (带回调操作):00:00:00.0983786
有点奇怪的是,在数组结构上,带回调自定义函数时间消耗反而比不带回调的低一点?
所以可以确定一下性能排序分别为:
string.concat->string.Join->StringBuilder 自定义拼接 ->+ 号拼接
(其中 concat 之所以性能更高,除了因为少了一位『分隔符』的插入,看源码似乎还利用了创建一个最终大小字符串,通过内存拷贝方式复制进去实现)
这么看起来,还是内置拼接函数性能比较高。
不过 concat、Join 的局限性在于:只能用于数组类型,且只处理字符串 —— 如果对象不是字符串,则直接通过 ToString 强转为字符串进行拼接。(要是有某个非字符串数组类型对象重载过 ToString 输出正确值也不是不能用)
# 4. 第二版优化
经过测试之后,大概性能也有点数了。
于是就有一些新的想法:例如无回调需求时使用 join 拼接、分隔符为空则采用 concat 拼接 —— 虽然会增加一点判断,但是性能该是可以提升一点的。
另外在目前自定义扩展函数的使用方式上,感觉也还有点缺点:比如字典类型,如果别人想把 k、v 结构也拼接在一块,那么这里就不大好办了,让调用者在回调方法用 + 号拼接一次?这样可就又冗余了。所以最好也提供一个重载使其作为可选项。
最终形成以下方法:
private static StringBuilder _stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(32); | |
private static int _stringCacheLength; | |
private static int _stringCacheTopIndex; | |
/// <summary> | |
/// 将数组组合为字符串 | |
/// </summary> | |
public static string toString<T>(this T[] arr, string separator = ",", Func<T, string> getStrCallback = null) | |
{ | |
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(separator) && getStrCallback == null) return string.Concat(arr); | |
//if (getStrCallback == null) return string.Join(separator, arr); | |
if (arr == null || arr.Length == 0) return ""; | |
_stringBuilder.Length = 0; | |
_stringCacheLength = arr.Length; | |
_stringCacheTopIndex = _stringCacheLength - 1; | |
for (int i = 0; i < _stringCacheLength; i++) | |
{ | |
_stringBuilder.Append(CheckDeliverValue(arr[i], getStrCallback)); | |
if (i != _stringCacheTopIndex) _stringBuilder.Append(separator); | |
} | |
return _stringBuilder.ToString(); | |
} | |
/// <summary> | |
/// 将列表组合为字符串 | |
/// </summary> | |
public static string toString<T>(this List<T> list, string separator = ",", Func<T, string> getStrCallback = null) | |
{ | |
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(separator) && getStrCallback == null) return string.Concat(list); | |
//if (getStrCallback == null) return string.Join(separator, list); | |
if (list == null || list.Count == 0) return ""; | |
_stringBuilder.Length = 0; | |
_stringCacheLength = list.Count; | |
_stringCacheTopIndex = _stringCacheLength - 1; | |
for (int i = 0; i < _stringCacheLength; i++) | |
{ | |
_stringBuilder.Append(CheckDeliverValue(list[i], getStrCallback)); | |
if (i != _stringCacheTopIndex) _stringBuilder.Append(separator); | |
} | |
return _stringBuilder.ToString(); | |
} | |
/// <summary> | |
/// 将字典的所有 value 组合为字符串,忽略字典的 Key 值 | |
/// </summary> | |
/// <param name="separator"> 分隔符 & lt;/param> | |
/// <param name="getValueStrCallback"> 如果 value 转化为字符串需要其它接口,可使用回调返回调用后的值 & lt;/param> | |
/// <returns>value,value,value,value,value......</returns> | |
public static string toString<K, V>(this Dictionary<K, V> dic, string separator = ",", Func<V, string> getValueStrCallback = null) | |
{ | |
return toString(dic, separator, null, null, getValueStrCallback); | |
} | |
/// <summary> | |
/// 将字典 key 和 value 成对组合为字符串,需要传入对应的分隔符 | |
/// </summary> | |
/// <param name="separator"> 每个对象之间分割符 & lt;/param> | |
/// <param name="separatorKV">key 和 value 分隔符,传入空值拼接时将忽略 key 值 & lt;/param> | |
/// <param name="getKeyStrCallback"> 如果 key 转化为字符串需要其它接口,可使用回调返回调用后的值 & lt;/param> | |
/// <param name="getValueStrCallback"> 如果 value 转化为字符串需要其它接口,可使用回调返回调用后的值 & lt;/param> | |
/// <returns > 默认:key:value,key:value,key:value......</returns> | |
public static string toString<K, V>(this Dictionary<K, V> dic, string separator, string separatorKV, Func<K, string> getKeyStrCallback = null, Func<V, string> getValueStrCallback = null) | |
{ | |
if (dic == null || dic.Count == 0) return ""; | |
_stringBuilder.Length = 0; | |
//kv 分隔符为空,则当做表示不拼接 key | |
bool appendKey = !string.IsNullOrEmpty(separatorKV); | |
foreach (var item in dic) | |
{ | |
// 附加字典 key | |
if (appendKey) | |
{ | |
_stringBuilder.Append(CheckDeliverValue(item.Key, getKeyStrCallback)); | |
_stringBuilder.Append(separatorKV); | |
} | |
// 附加字典值 | |
_stringBuilder.Append(CheckDeliverValue(item.Value, getValueStrCallback)); | |
// 分隔符 | |
_stringBuilder.Append(separator); | |
} | |
_stringBuilder.Remove(_stringBuilder.Length - 1, 1); | |
return _stringBuilder.ToString(); | |
} | |
/// <summary> | |
/// 将数组组合为字符串,换行分割 | |
/// </summary> | |
public static string toStringLine<T>(this T[] arr, Func<T, string> getStrCallback = null) | |
{ | |
return arr.toString(Environment.NewLine, getStrCallback); | |
} | |
/// <summary> | |
/// 将列表组合为字符串,换行分割 | |
/// </summary> | |
public static string toStringLine<T>(this List<T> list, Func<T, string> getStrCallback = null) | |
{ | |
return list.toString(Environment.NewLine, getStrCallback); | |
} | |
/// <summary> | |
/// 将字典组合为字符串,换行分割 (忽略 key 值) | |
/// </summary> | |
public static string toStringLine<K, V>(this Dictionary<K, V> dic, Func<V, string> getStrCallback = null) | |
{ | |
return dic.toString(Environment.NewLine, getStrCallback); | |
} | |
/// <summary> | |
/// 检查是否对值进行回调处理(若 getValueStrCallback 不为空则返回调用后结果,参数为 value) | |
/// </summary> | |
private static string CheckDeliverValue<T>(T value, Func<T, string> getValueStrCallback) | |
{ | |
if (getValueStrCallback == null) return value.ToString(); | |
return getValueStrCallback(value); | |
} |
# 性能测试:
依然是 100000 个随机字符串,循环一百次拼接。
测试代码:
// 测试内部函数 concat 拼接数组 | |
DoTest("string.concat 拼接数组", () => string.Concat(_strArray)); | |
//2. 测试内部函数 join 拼接数组 | |
DoTest("string.Join 拼接数组", () => string.Join(",", _strArray)); | |
//3. 测试自定义函数拼接数组 | |
DoTest("自定义函数拼接数组", () => _strArray.toString()); | |
//4. 测试带回调自定义函数拼接数组 | |
DoTest("带回调自定义函数拼接数组", () => _strArray.toString(",", str => str)); | |
//5. 测试 join 函数拼接列表 | |
DoTest("string.Join 拼接列表", () => _strList.toString()); | |
//6. 测试自定义函数拼接列表 | |
DoTest("自定义函数拼接列表", () => _strList.toString()); | |
//7. 测试带回调自定义函数拼接列表 | |
DoTest("带回调自定义函数拼接列表", () => _strList.toString()); | |
//8. 测试自定义函数拼接类类型 | |
DoTest("自定义函数拼接类类型", () => _strClassArray.toString(",", data => data.GetDes())); | |
//9. 测试自定义函数拼接字典 | |
DoTest("自定义函数拼接字典", () => _strDic.toString()); | |
//10. 测试自定义函数拼接字典 | |
//DoTest ("自定义函数拼接字典 (带回调操作)", () => _strDic.toString (","); | |
DoTest("string.concat 拼接数组", () => string.Concat(_strArray)); | |
DoTest("string.join 拼接数组", () => string.Join(",", _strArray)); | |
DoTest("拼接数组(无分隔符)", () => _strArray.toString(string.Empty)); | |
DoTest("拼接数组", () => _strArray.toString()); | |
DoTest("拼接数组(带回调)", () => _strArray.toString(",", str => str)); | |
DoTest("拼接字典 Value", () => _strDic.toString()); | |
DoTest("拼接字典(带 Value 回调)", () => _strDic.toString(",", v => v)); | |
DoTest("拼接字典 K、V", () => _strDic.toString(",", ":")); | |
DoTest("拼接字典 K、V(带 Key 回调)", () => _strDic.toString(",", ":", k => k.ToString())); | |
DoTest("拼接字典 K、V(带 Key、Value 回调)", () => _strDic.toString(",", ":", k => k.ToString(), v => v)); | |
DoTest("拼接字典(字典转数组拼接)", () => _strDic.ToArray().toString()); | |
DoTest("拼接字典(字典转列表拼接)", () => _strDic.ToList().toString()); |
- string.concat 拼接数组:0 秒 937 毫秒
- string.Join 拼接数组:1 秒 282 毫秒
- 自定义函数拼接数组:1 秒 837 毫秒
- 带回调自定义函数拼接数组:1 秒 809 毫秒
- string.Join 拼接列表:1 秒 858 毫秒
- 自定义函数拼接列表:1 秒 916 毫秒
- 带回调自定义函数拼接列表:1 秒 847 毫秒
- 自定义函数拼接类类型:10 秒 400 毫秒
- 自定义函数拼接类类型 (GetDes () 无计算):1 秒 870 毫秒
- 自定义函数拼接字典:2 秒 316 毫秒
- string.concat 拼接数组:0 秒 910 毫秒
- string.join 拼接数组:1 秒 253 毫秒
- 拼接数组 (无分隔符):1 秒 638 毫秒
- 拼接数组:1 秒 764 毫秒
- 拼接数组 (带回调):1 秒 794 毫秒
- 拼接字典 Value:2 秒 332 毫秒
- 拼接字典 (带 Value 回调):2 秒 356 毫秒
- 拼接字典 K、V:8 秒 121 毫秒
- 拼接字典 K、V (带 Key 回调):8 秒 111 毫秒
- 拼接字典 K、V (带 Key、Value 回调):8 秒 335 毫秒
- 拼接字典 (字典转数组拼接):14 秒 391 毫秒
- 拼接字典 (字典转列表拼接):15 秒 655 毫秒
(低版本 C# 的 string.concat、string.Join 连列表都不支持,甚至只能用在字符串数组上,所以上边说检测到对应情况 (没有分隔符或纯字符串数组) 后执行系统拼接函数只能在高版本下使用)
[concat 由于低版本 C# 不支持除纯字符串数组之外的对象且有 object 重载,泛型数组也是可以直接丢进去的,然而直接当做 object.ToString 返回了,测试时发现消耗时间短得不可思议,仔细看才发现不对,例如上述『拼接列表 (无分隔符)』就是走进这个分支判断的情况,只能先注释掉]
# 5. StringBuilder 源码
另外稍微看了下源码,StringBuilder 默认初始化 16 个字符大小的数组:
// Token: 0x060065BB RID: 26043 RVA: 0x00155704 File Offset: 0x00153904 | |
[__DynamicallyInvokable] | |
public StringBuilder() : this(16) | |
{ | |
} | |
// Token: 0x060065BC RID: 26044 RVA: 0x0015570E File Offset: 0x0015390E | |
[__DynamicallyInvokable] | |
public StringBuilder(int capacity) : this(string.Empty, capacity) | |
{ | |
} | |
// Token: 0x060065D7 RID: 26071 RVA: 0x001561B8 File Offset: 0x001543B8 | |
[ComVisible(false)] | |
[__DynamicallyInvokable] | |
public StringBuilder AppendLine(string value) | |
{ | |
this.Append(value); | |
return this.Append(Environment.NewLine); | |
} |
容量足够的情况下,通过 unsafe 方法进行指针及直接内存操作:
- 获取添加的字符串指针
- 获取字符数组待添加下标指针
- 调用 Buffer.Memcpy 进行内存拷贝进字符数组
如果后续容量不够,则进行动态扩容:
// Token: 0x060065D1 RID: 26065 RVA: 0x0015603C File Offset: 0x0015423C | |
[SecuritySafeCritical] | |
[__DynamicallyInvokable] | |
public unsafe StringBuilder Append(string value) | |
{ | |
if (value != null) | |
{ | |
char[] chunkChars = this.m_ChunkChars; | |
int chunkLength = this.m_ChunkLength; | |
int length = value.Length; | |
int num = chunkLength + length; | |
if (num < chunkChars.Length) | |
{ | |
// 容量足够 | |
} | |
else | |
{ | |
// 走扩容 | |
this.AppendHelper(value); | |
} | |
} | |
return this; | |
} |
不过动态扩容不是直接扩容字符数组,而是通过单向链表的方式:
// Token: 0x06006615 RID: 26133 RVA: 0x0015730C File Offset: 0x0015550C | |
private void ExpandByABlock(int minBlockCharCount) | |
{ | |
if (minBlockCharCount + this.Length < minBlockCharCount || minBlockCharCount + this.Length > this.m_MaxCapacity) | |
{ | |
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("requiredLength", Environment.GetResourceString("ArgumentOutOfRange_SmallCapacity")); | |
} | |
int num = Math.Max(minBlockCharCount, Math.Min(this.Length, 8000)); | |
this.m_ChunkPrevious = new StringBuilder(this); | |
this.m_ChunkOffset += this.m_ChunkLength; | |
this.m_ChunkLength = 0; | |
if (this.m_ChunkOffset + num < num) | |
{ | |
this.m_ChunkChars = null; | |
throw new OutOfMemoryException(); | |
} | |
this.m_ChunkChars = new char[num]; | |
} |
将当前数据全部转移至『上一个』节点,然后自己创建一个新的字符数组进行处理。
除 StringBuilder 本身外,string 类提供的一些静态操作方法也再次利用 StringBuilder 对性能进行优化,如 join、format 底层都会调到那边去,还采用了 StringBuilderCache 对象池。
# 6. Join 部分源码
// Token: 0x060004B8 RID: 1208 RVA: 0x00010B4C File Offset: 0x0000ED4C | |
[SecuritySafeCritical] | |
[__DynamicallyInvokable] | |
public unsafe static string Join(string separator, string[] value, int startIndex, int count) | |
{ | |
//======= 省略判断 ================ | |
// 字符串类型数组,直接通过分配一大块字符串内存,通过 unsafe 内存拷贝实现 | |
string text = string.FastAllocateString(num); | |
fixed (char* ptr = &text.m_firstChar) | |
{ | |
UnSafeCharBuffer unSafeCharBuffer = new UnSafeCharBuffer(ptr, num); | |
unSafeCharBuffer.AppendString(value[startIndex]); | |
for (int j = startIndex + 1; j <= num2; j++) | |
{ | |
unSafeCharBuffer.AppendString(separator); | |
unSafeCharBuffer.AppendString(value[j]); | |
} | |
} | |
return text; | |
} | |
// 连接迭代器 (列表类型) 通过 StringBuilder 进行 | |
// Token: 0x060004B5 RID: 1205 RVA: 0x000109C4 File Offset: 0x0000EBC4 | |
[ComVisible(false)] | |
[__DynamicallyInvokable] | |
public static string Join<T>(string separator, IEnumerable<T> values) | |
{ | |
// 省略部分处理代码 | |
result = StringBuilderCache.GetStringAndRelease(stringBuilder); | |
return result; | |
} | |
// 连接 object 数组类型,通过 StringBuilderCache 对象池取 StringBuilder 进行拼接 | |
// Token: 0x060004B4 RID: 1204 RVA: 0x0001093C File Offset: 0x0000EB3C | |
[ComVisible(false)] | |
[__DynamicallyInvokable] | |
public static string Join(string separator, params object[] values) | |
{ | |
// 省略 | |
return StringBuilderCache.GetStringAndRelease(stringBuilder); | |
} |
# 7. string.Concat
// 当连接数量级比较低时,参数为 string 则直接通过创建最终字符串内存连接 | |
// Token: 0x06000556 RID: 1366 RVA: 0x00013524 File Offset: 0x00011724 | |
[SecuritySafeCritical] | |
[__DynamicallyInvokable] | |
public static string Concat(string str0, string str1) | |
{ | |
// 部分判断代码省略 =============== | |
int length = str0.Length; | |
string text = string.FastAllocateString(length + str1.Length); | |
string.FillStringChecked(text, 0, str0); | |
string.FillStringChecked(text, length, str1); | |
return text; | |
} | |
// 连接迭代器 (列表类型) 通过 StringBuilder 进行 | |
// Token: 0x06000555 RID: 1365 RVA: 0x000134B8 File Offset: 0x000116B8 | |
[ComVisible(false)] | |
[__DynamicallyInvokable] | |
public static string Concat(IEnumerable<string> values) | |
{ | |
// 省略 | |
return StringBuilderCache.GetStringAndRelease(stringBuilder); | |
} | |
// 当连接数量级比较低时,参数为 object 则直接通过符号连接 | |
// Token: 0x06000551 RID: 1361 RVA: 0x00013330 File Offset: 0x00011530 | |
[__DynamicallyInvokable] | |
public static string Concat(object arg0, object arg1, object arg2) | |
{ | |
// 判断省略 ========== | |
return arg0.ToString() + arg1.ToString() + arg2.ToString(); | |
} | |
//ConcatArray (当 string.Concat 超过三个 object 对象时调用) | |
// 超出这个数量则通过内存分配进行 | |
// Token: 0x06000559 RID: 1369 RVA: 0x000136AC File Offset: 0x000118AC | |
[SecuritySafeCritical] | |
private static string ConcatArray(string[] values, int totalLength) | |
{ | |
string text = string.FastAllocateString(totalLength); | |
int num = 0; | |
for (int i = 0; i < values.Length; i++) | |
{ | |
string.FillStringChecked(text, num, values[i]); | |
num += values[i].Length; | |
} | |
return text; | |
} |
直接分配指定字符串数组所有字符串长度大小的大块字符串,然后通过 wstrcpy->Buffer.Memcpy 对内存直接进行拷贝操作。
# 8. Format
private static string FormatHelper(IFormatProvider provider, string format, ParamsArray args) | |
{ | |
if (format == null) | |
{ | |
throw new ArgumentNullException("format"); | |
} | |
return StringBuilderCache.GetStringAndRelease(StringBuilderCache.Acquire(format.Length + args.Length * 8).AppendFormatHelper(provider, format, args)); | |
} |
# 对 string.Format 与普通拼接的性能测试
除了对数组一类数据结构类型的拼接之外,常用的估计就 2~3 个带参数的简单字符串拼接了。
这种通常见到的还是直接 + 号进行,也有使用 string.Format 的。
为了评估以后究竟以使用哪种方式为准,我想再加一点测试,测一测使用 + 号与 string.Format 拼接简单字符串两者的性能。
每一项进行 10000 次操作,测试结果如下:
- 简单拼接测试(X+1):0 秒 3 毫秒
- 简单拼接测试(1+X):0 秒 3 毫秒
- 简单拼接测试(X+1+Y):0 秒 4 毫秒
- 简单拼接测试(X+1+Y+2):0 秒 6 毫秒
- 简单拼接测试(X+1+Y+2+Z+3):0 秒 11 毫秒
- 简单拼接测试(X+1+Y+2+Z+3+W+4):0 秒 14 毫秒
- string.concat(X+1):0 秒 3 毫秒
- string.concat(1+X):0 秒 3 毫秒
- string.concat(X+1+Y):0 秒 4 毫秒
- string.concat(X+1+Y+2):0 秒 6 毫秒
- string.concat(X+1+Y+2+Z+3):0 秒 26 毫秒
- string.concat(X+1+Y+2+Z+3+W+4):0 秒 14 毫秒
- string.format 拼接测试(X {0}):0 秒 7 毫秒
- string.format 拼接测试({0} X):0 秒 7 毫秒
- string.format 拼接测试(X {0} Y):0 秒 7 毫秒
- string.format 拼接测试(X {0} Y {1}):0 秒 11 毫秒
- string.format 拼接测试(X {0} Y {1} Z {2}):0 秒 16 毫秒
- string.format 拼接测试(X {0} Y {1} Z {2} W {3}):0 秒 35 毫秒
- StringBuilder 拼接测试(X+1):0 秒 4 毫秒
- StringBuilder 拼接测试(1+X):0 秒 4 毫秒
- StringBuilder 拼接测试(X+1+Y):0 秒 5 毫秒
- StringBuilder 拼接测试(X+1+Y+2):0 秒 8 毫秒
- StringBuilder 拼接测试(X+1+Y+2+Z+3):0 秒 11 毫秒
- StringBuilder 拼接测试(X+1+Y+2+Z+3+W+4):0 秒 14 毫秒
每一项进行 100000 次操作,去除随机参数,测试结果如下:
- 简单拼接测试(X+1):0 秒 16 毫秒
- 简单拼接测试(1+X):0 秒 15 毫秒
- 简单拼接测试(X+1+Y):0 秒 20 毫秒
- 简单拼接测试(X+1+Y+2):0 秒 25 毫秒
- 简单拼接测试(X+1+Y+2+Z+3):0 秒 66 毫秒
- 简单拼接测试(X+1+Y+2+Z+3+W+4):0 秒 77 毫秒
- string.concat(X+1):0 秒 17 毫秒
- string.concat(1+X):0 秒 16 毫秒
- string.concat(X+1+Y):0 秒 35 毫秒
- string.concat(X+1+Y+2):0 秒 24 毫秒
- string.concat(X+1+Y+2+Z+3):0 秒 65 毫秒
- string.concat(X+1+Y+2+Z+3+W+4):0 秒 64 毫秒
- string.format 拼接测试(X {0}):0 秒 60 毫秒
- string.format 拼接测试({0} X):0 秒 66 毫秒
- string.format 拼接测试(X {0} Y):0 秒 68 毫秒
- string.format 拼接测试(X {0} Y {1}):0 秒 71 毫秒
- string.format 拼接测试(X {0} Y {1} Z {2}):0 秒 106 毫秒
- string.format 拼接测试(X {0} Y {1} Z {2} W {3}):0 秒 145 毫秒
- StringBuilder 拼接测试(X+1):0 秒 28 毫秒
- StringBuilder 拼接测试(1+X):0 秒 27 毫秒
- StringBuilder 拼接测试(X+1+Y):0 秒 33 毫秒
- StringBuilder 拼接测试(X+1+Y+2):0 秒 38 毫秒
- StringBuilder 拼接测试(X+1+Y+2+Z+3):0 秒 67 毫秒
- StringBuilder 拼接测试(X+1+Y+2+Z+3+W+4):0 秒 62 毫秒
结果非常出乎意料,原以为 string.format 性能应该是比较好的,没成想竟然是最费的... 也许由于字符串内部占位符需要单独做解析,导致了大量消耗?
于是看了下源码,发现在 AppendFormatHelper 方法中,对整个字符串都做了一次遍历,去分析是否有 {} 这种占位符,这个确实是个会随字符串量级增加而增加消耗的一个操作 ——string.format 对于连接字符串存在多个参数的情况下,耗费时间也同样会随着参数增长而增加。
因此除了字符串数组类型拼接方法外,可以自己专门定义一个方法用于连接『散』字符串,以选择性能更好的拼接方式。
# 总结
根据上面的测试 —— 虽然这种测试不一定很准确 (毕竟 Unity 中 .Net 版本比较低),以及对 string 源码本身的查看,基本上可以总结以下几个注意点:
连接纯字符串超过 3 个时,有分隔符可以选择 StringBuilder、string.join (数组),否则使用 string.concat (数组),至于 string.format—— 除了好看一点,能不用就不要用了,性能上完全没有优势。
其中 string.concat 及 string.join 的源码显示,其对不同类型选择了不同的处理方式。
共同点有:
- 字符串类型数组,直接通过分配一大块字符串内存,通过 unsafe 内存拷贝实现
- 连接迭代器 (列表类型) 或者连接 object 数组均通过 StringBuilderCache 取 StringBuilder 进行
string.Concat 特有:
- 参数为 string,当连接数量级比较低时,直接通过分配一块最终字符串大小内存,通过 unsafe 内存拷贝实现
- 参数为 object,当连接数量级比较低时 (3 个以下), 则直接通过符号连接,超过三个则创建临时数组变量将 object 转字符串,再走正常字符串数组连接方法
# 最终可以得出结论:
拼接数量在 2 个:可以使用 + 号
拼接数量在 4 个及以下:字符串可以使用 string.concat (非字符串 3 个或以下时直接 + 号拼接,4 个或以上时会生成临时数组变量将 object.tostring,然后调用字符串数组拼接函数处理 —— 调用不定参数方法时也是如此处理),否则最好 StringBuilder
拼接数量在超过 4 个:StringBuilder (不推荐 string.concat 是因为通过可变参数传参它会生成额外临时字符串数组,直接拼接数组时更有优势)
连接字符串数组、字符串列表类型:可以用 string.join 或 string.concat (无分隔符),有特殊回调需求则自定义 StringBuilder (注:内部实际上也是用 StringBuilder 拼接的,不过看 DotNetCore 的源码实现不一样,是创建一个结构体 ValueStringBuilder,通过 stackalloc 在栈上分配 char 数组 (Span) 结构进行拼接)
连接其它容器 (比如字典):StringBuilder
再解释一下:
连接字符串在 4 个及以下时,可以通过 string.concat (强调:字符串类型,非字符串可以 toString 传入)
字符串数组和字符串列表都可以用 string.join 或 string.concat (内部 StringBuilder ,有对象池)
其它类型的数组、列表或字典容器以及超出 4 个单字符串的连接,采用自己 StringBuilder 进行,并且可以缓存这个 StringBuilder 进行重复使用。
只有两个字符串拼接,才允许使用符号 +
(注:上述均表示一次性拼接的前提,若连续多次连接,则 StringBuilder 无疑是最好选择)
